Strategic Diversity Leadership
In “Strategic Diversity Leadership: The Role of Senior Leaders in Delivering the Diversity Dividend” (Journal of Management, September 2020), Luis L. Martins shines a spotlight on the role that top executives play in shaping organizational culture and driving organizational performance. In this paper, he discusses his findings from an extensive literature review of contemporary research on strategic leadership and workplace diversity and inclusion, work that led him to develop a new framework he calls “strategic diversity leadership.” His purpose is to share this framework with organizational leaders who are seeking competitive advantage as well as his academic peers to inspire further study.
As a professor and chair of the management department at The University of Texas at Austin, Martins knows a thing or two about organizational cultures and organizational performance. Over a 30-year academic career, he has conducted research and written extensively on the factors that drive innovation, change, and performance, including diversity and inclusion. He has also consulted for dozens of clients, such as Coca Cola, FBI Crime Labs, Samsung, and Waffle House, to test solutions in the real world. Business and academic leaders know that when Martins finds a new way of solving a problem, it is worth taking a closer look.
A missing link
There is a significant body of research that shows diversity leads to better organizational performance, but there is also evidence that shows the implementation of diversity and inclusion programs do not always lead to the desired results. Martins defines the diversity dividend as “the enhancement in an organization’s performance that is attributable to its diversity” (1192). When he investigates why the diversity dividend is not realized, he discovers a missing link between the traditional role of top executives and the role they must play in their organization’s diversity and inclusion efforts. If Martins is right, which I believe he is, implementing a strategic diversity leadership framework to close this gap is the key to better performance.
Leaders must lead
Martins defines strategic diversity leadership as “the shaping of the meaning of diversity within an organization by the organization’s senior leaders” (1194). Martins’ strategic diversity leadership framework is extremely useful because it directly links the role of senior leaders to the efforts and outcomes associated with the organization’s diversity and inclusion initiatives. Because they hold positions of authority, Martins asserts, top executives have both the platform and the responsibility for realizing the benefits of a diverse workforce. That is to say, supervisors and other employees can only do so much if the organization’s top executives do not lead the way.
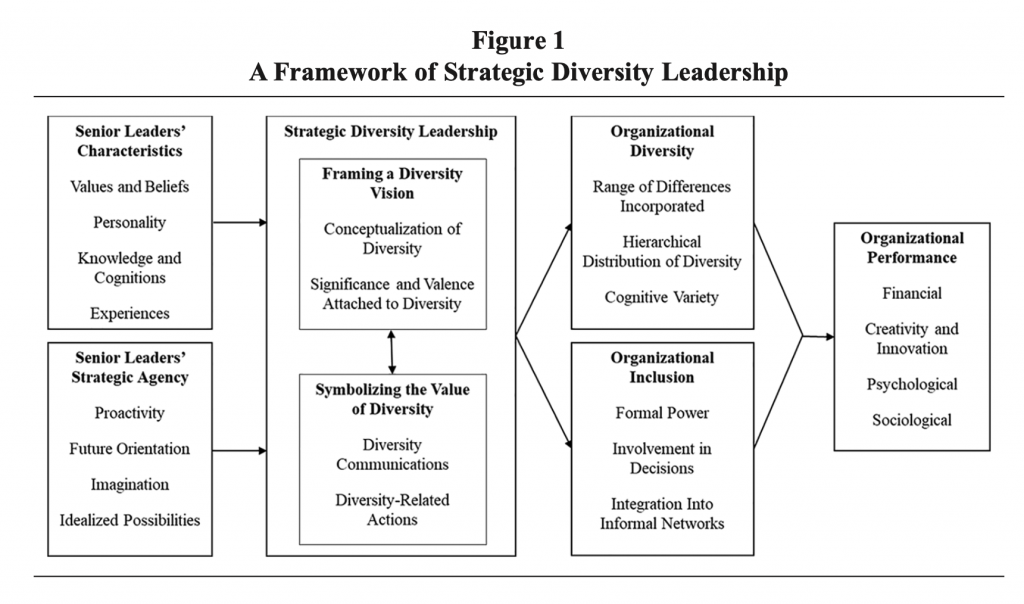
Martins argues that senior leaders must use the power of communication to establish a vision and articulate that the “current state is unacceptable” (1198). He also argues that senior leaders must participate in public activities that promote diversity and inclusion, including rituals and ceremonies (1198-1199). In other words, top executives must symbolize the value of diversity and inclusion through both words and actions. Only by taking full responsibility for the design of the organizational culture can senior leaders create organizational performance that maximizes the diversity dividend.
The strategic diversity leadership framework Martins proposes is important because it shifts our focus for solving organizational culture challenges from the level of supervisors, staff, policies, and tasks to the level of executives, vision, strategy, and organizational design. Martins is telling us that those who hold the most power in an organization also hold the most responsibility and they must be held accountable. I couldn’t agree more. While the strategic diversity leadership framework holds great potential for bringing about change, Martins understands that he is breaking new ground and proposes further study to finetune his theories and reveal additional insights. I look forward with optimism to seeing his ideas confirmed.
Works Cited
Martins, Luis L. “Strategic Diversity Leadership: The Role of Senior Leaders in Delivering the Diversity Dividend.” Journal of Management, 1 September 2020, pp. 1191-1204, https://doi-org.libezproxy2.syr.edu/10.1177/0149206320939641.
“Luis Martins Biography.” The University of Texas at Austin, McCombs School of Business. https://www.mccombs.utexas.edu/execed/faculty/luis-martins.


