As you’re continuing with your research, I encourage you to remember this: research is a creative process.
Here’s why that matters:
- whatever your topic, whatever your motivation, when you research you are making something new–a new set of ideas, new questions, a new collection of perspectives
- because research is a creative endeavor, there isn’t a single *right* way to do it–you’re not assembling an Ikea bookshelf; you’re creating something brand new that hasn’t been before and that is unlike anyone else’s project (and it’s totally fine to have leftover parts 😉 )
- when you’re entering new, uncharted territory, it’s helpful to have models and maps–tutorials for different search tools (such as the SU Libraries how-to pages) offer a lot of value, in addition to the notetaking and analytical reading work we’ve been doing in class
- you can have fun with this work–you’re charting your own course to a large extent, and you can be inventive with your choice of sources (inputs) and products (outputs)
The note-taking work that you’ve been doing this past week is part of this generative process. As you read, think critically, and respond to your sources’ ideas in your notes, you are beginning to shape your own perspective on the subject at hand, and ultimately your own contribution to the larger body of thought on this subject. That’s why I’m asking you to spend some real time on taking notes. Note-taking is where your creative thought-work begins.
A few suggestions to keep in mind:
- use tools for what they’re good for: the SU Libraries website is good for finding specialized material by scholars and other experts. It will also give you full-text access to newspapers from all over the world. When you’re looking for that stuff, go there. Primary sources sometimes pop up there, but are more likely to be found on the open web, where anyone can publish. When you’re looking for that stuff, it makes sense to start with Google.
- keep in mind that sources come in many forms–not just articles and books, but radio features, podcasts, images, documentaries and other videos, interviews/Q&As, etc. You’re not limited to traditional kinds of texts.
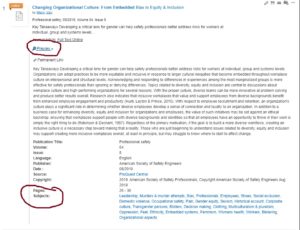
- jump straight to Advanced Search–filter your results more on the front end, and you’ll have fewer to sift through. Consider adding multiple search terms and placing limits on date, type of publication, language, etc. Note that when adding search terms in Advanced Search, you have a dropdown menu that defaults to “All Fields” (term appears anywhere in the text). You can also select “abstract” (term is significant enough to appear in the summary of the text). See the image below:
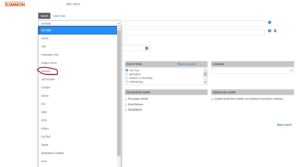
- use sources to leapfrog–check out authors’ bibliographies for ideas, pay attention to the Subject headings or Keywords in the citation entry of a database search. Check out the image below–in your list of search results, hover over the Preview+ option to pull up the full citation, and then check out the Subjects listed–these are the terms this database uses to catalog related material. You can incorporate these as search terms, and it’s kind of like browsing the physical shelf in the library for other similar materials.